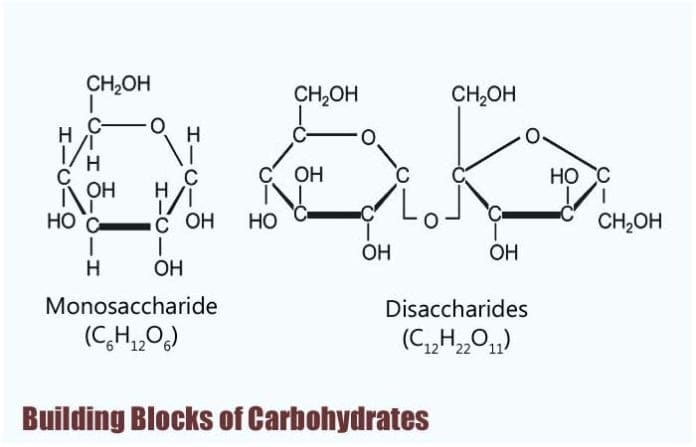
Describe the Building Blocks of Carbohydrates
Open the link study the diagram in 25 seconds and describe the details what the image is showing. Enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks to facilitate their absorption by the body.

Monosaccharides Simple Sugars Definition List Examples Of Foods Biochemistry Biology Notes Biology
Simple sugars such as glucose and fructose are the building components.
. Look at the given list of 20 PTE Describe Image Sample Tests below. Atoms are the building blocks of molecules each and everything in this world is build up of atoms. Different organs play specific roles in the digestive process.
About 20 different amino acids combine to form all of the various types of proteins on Earth. Examples of carbohydrates include starch fiber the sweet-tasting compounds called sugars and structural materials such as cellulose. Unless you are eating it raw the first step in egg.
Proteins are the building blocks of our body. Your heart rhythm is usually determined by coordinated electrical activation but when electrical signals that coordinate that rhythm are not working correctly. Fat in food serves as an energy source with high caloric density adds texture and taste and contributes to.
The building blocks of all carbohydrates are the monosaccharides. Lipids perform functions both within the body and in food. However taking excess amount of protein can be of no use and cause damage to your body.
Monosaccharides are a type of polymer-forming monomers. Atoms cant be see in a light microscope they are very very small typically 1 billionth of a meter. Shown below are Fischer projection formulas for a group of common monosaccharides.
Figure 67 Digestion and Absorption of Protein. The only difference is the R group which differs in each of the amino acids and gives them their uniqueness. Carbons in the sugar are represented with the elemental symbol C at the end of the chain but also are represented by vertices such as.
These amino acids all have almost the exact same composition. Proteins primary function is to build and maintain body structures such as muscle bones and internal organs and to synthesize important molecules such as antibodies enzymes neurotransmitters and various blood proteins according to the NLM. They contain monomers and polymers as building blocks.
The three major classes of nutrients that undergo digestion are proteins lipids fats and carbohydrates. Fischer projection formulas are similar but not identical to organic structural formulas. The incorporation of carbon dioxide into organic compounds is known as carbon fixation.
Eggs are a good dietary source of protein and will be used as our example to describe the path of proteins in the processes of digestion and absorption. The term carbohydrate had its origin. Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and identify the types of lipids typically found in bacterial membranes.
List and describe the role of lipids in food. Distinguish macroelements macronutrients from micronutrients trace elements and provide examples of each. You have 40 seconds to give your response.
Compare and contrast passive diffusion. Digestive enzymes are enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. From the Mouth to the Stomach.
When a protein is made the protein comes together one amino. Provide examples of growth factors needed by some microorganisms. Carbohydrates are one of lifes four fundamental macromolecules.
The animal diet needs carbohydrates protein and fat as well as vitamins and inorganic components for nutritional balance. A disaccharide is made up of two monosacchari. Answer these PTE describe image practice questions.
One egg whether raw hard-boiled scrambled or fried supplies about six grams of protein. Protein is composed of building blocks called amino acids. There are different atom types well come back to that later but each atom type is build in a similar way.
The energy for this comes from. All carbohydrates consist of carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms and are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or are compounds that can be broken down to form such compounds. PTE Describe Image Practice Test Series.
In the Light Independent Process carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or water for aquaticmarine organisms is captured and modified by the addition of Hydrogen to form carbohydrates general formula of carbohydrates is CH 2 O n. Within the body lipids function as an energy reserve regulate hormones transmit nerve impulses cushion vital organs and transport fat-soluble nutrients. The basic building blocks of all atoms are three basic pieces.
Building blocks called amino acids make up proteins. Article Correcting Heart Arrhythmia with Minimally Invasive Surgery.
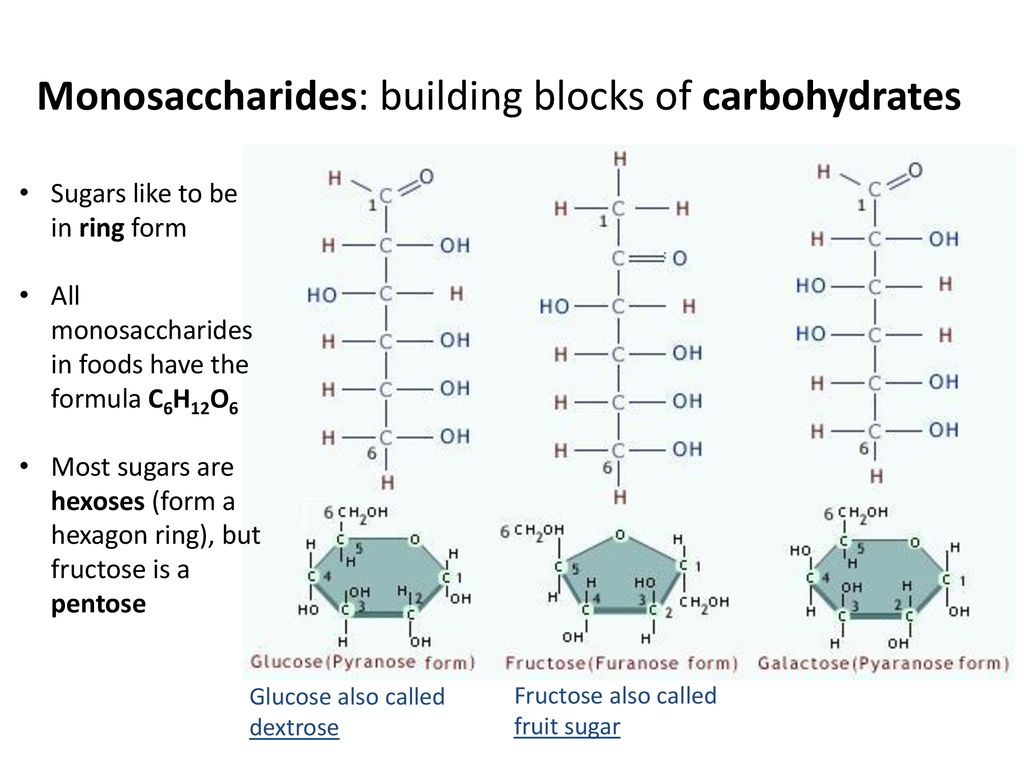
Monosaccharides Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates Ppt Download

Figure 11 11 Common Disaccharides Biochemistry Ncbi Bookshelf Teaching Chemistry Biochemistry Biology Notes
No comments for "Describe the Building Blocks of Carbohydrates"
Post a Comment